Heart Disease
-
A study of white-collar workers has found that men who experience work stress coupled with a job that requires high effort for low reward are at double the risk of developing heart disease, having a similar impact on heart health as obesity.
-
A high resting heart rate, considered anything above 100 beats per minute, has been linked to an elevated risk of serious cardiovascular conditions such as coronary artery disease and stroke. Knowing how genes impact this is vital for preventative care.
-
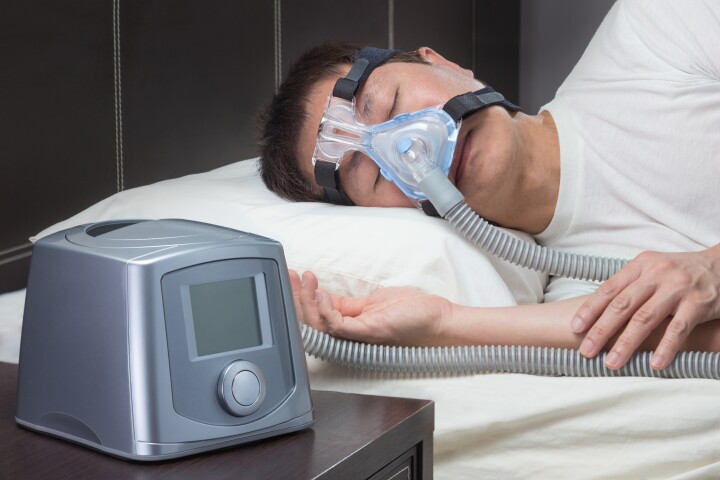
While effective in treating sleep apnea, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines are intrusive and disruptive, which is why 50% of patients give up on using the life-saving devices. A new study shows why they might be worth the discomfort.
-
Let's face it: food that tastes delicious is usually bad for us. But new research shows that a simple preparation trick can dramatically slash fat, sodium and added sugars while making foods like brownies and meatloaf taste just as good.
-
For the first time, scientists have identified a marker in the retina that may lead to Parkinson’s disease, and it can be detected early, which could be life-changing for those at risk of developing this or other degenerative conditions.
-
A new study has found that measuring the levels of white blood cells in your saliva through an easy 30-second mouth rinse is an effective way of detecting the warning signs of heart disease early, especially in young, otherwise healthy people.
-
Researchers have discovered the way that red blood cell particles interact with white blood cells called macrophages to reduce the formation of fatty deposits on arterial walls, offering a potential treatment for this common condition.
-
Researchers have developed an injectable form of DHA, an omega-3 fatty acid, that halts the progression of the arterial fatty plaques that can lead to heart attack and stroke. The novel treatment may one day be used to treat heart disease.
-
Sleep apnea affects around 30 million Americans, but it can be incredibly difficult to treat, even more so given that devices used to alleviate it are given up on by nearly half of those diagnosed. Scientists are now proposing a different approach.
-
Obesity is a massive global crisis, with around 650 million adults and 124 million children and adolescents impacted. Researchers from Cambridge University have made new discoveries about sex- and age-specific genetic hiccups related to obesity.
-
When you think exercise, holding your body still in a pose for a minute hardly springs to mind as a workout. But scientists have found that isometric moves such as wall sits and planks may be even better for your heart than both weights and cardio.
-
Researchers have used machine learning to assess bone density scans for calcification in the aorta, the body’s main artery. They say their method could be used to predict future cardiovascular and other disease, even before symptoms appear.
Load More